Cardano vs Polygon | Pros, Cons & Similarities in 2023

Both Cardano and Polygon, two of the most well-known cryptocurrency projects so far, are competing for market dominance in the rapidly growing blockchain industry. In order to help investors and other stakeholders (you!) make more informed judgments about these networks, this article compares both projects conceptually and technically in great detail. Get ready for 2023!
An Associated History
Because Polygon is an Ethereum Layer-2 (L2) solution, Cardano and Polygon have a shared past.
In 2013, Vitalik Buterin had the idea for Ethereum. Buterein enlisted the aid of Charles Hoskinson and a few others to develop the concept. However, the two couldn’t agree on whether the project should be for profit or nonprofit. Hoskinson quit the Ethereum project in late 2014 to start IOHK, a blockchain engineering and research firm. And Cardano quickly emerged as IOHK’s signature project.
Cardano, a “third generation” blockchain introduced in 2017, aims to outperform Ethereum in terms of cost, speed, and environmental impact. The same year, Polygon was established to assist Ethereum in achieving these similar goals. Today, Cardano and Polygon are two of the top 10 cryptocurrency projects by market capitalization (Market caps for Cardano vs Polygon are sourced from coinmarketcap.com, current as of 4:31 p.m. UTC on Jan. 31, 2023).
What Are Cardano and Polygon
Both are open source, decentralized, proof-of-stake (POS) blockchain networks. Both have smart contract logic for the development of third-party decentralized applications. Both provide users with fast transactions and low fees. However, there are major conceptual and technical differences.
- Cardano is a decentralized, POS, L1 blockchain protocol. Cardano’s development has been slow and purposeful as its subject to extensive peer-reviewed research. Cardano is being rolled out in stages and is currently in stage three (Goguen: Smart Contracts) of five total. Cardano’s ambitions are to scale into the global economy and transform multiple industries. Cardano’s native token is ADA.
- Polygon is a decentralized, POS, L2 multi-blockchain network for Ethereum. Polygon has a POS main-chain, but it also has a software framework that allows third-party developers to create new L2 chains that work with its main-chain and Ethereum. Polygon’s mission is to bolster Ethereum by reducing the latter’s gas fees and increasing its transaction output. Polygon’s native token is MATIC.
How Do Cardano and Polygon Work
Cardano and Polygon deploy POS consensus mechanisms, but each use different POS sub-variants, as well as other differing technologies to create their unique blockchains.
Cardano Technicals
- Ouroboros POS: “Ouroboros” is the ancient symbol of the snake that eats its own tail. Ouroboros POS implements a Global Random Oracle (GRO), which is a randomness algorithm that itself randomly changes over time. GRO leverages previous block data in part to produce each new iteration of randomness – hence the parallel to the legendary symbol. Ultimately, GRO is used for the secure selection of Cardano’s block validators. The algorithm is believed to provide enhanced security due to the extreme difficulty in anyone being able to predict the next block validator.
- Epochs and Slots: The Cardano blockchain is divided into epochs (approx. 4 days) and slots (approx. 20 seconds). The latter occurs inside the former. Ouroboros randomly selects nodes (selection odds are based in proportion to how much is staked) to validate new blocks for each slot. These selected nodes are known as “slot leaders”. Given an epoch can contain 432,000 slots, Cardano is able to process approximately 250 transactions per second.
- Two-Layered Architecture: Cardano operates in two layers. The Cardano Settlement Layer processes and records all ADA transactions. The Cardano Computation Layer processes the smart contract logic for the operation of the network’s decentralized applications.
Polygon Technicals
- Proof of Stake: Polygon’s main-chain uses a decentralized network of 100 permissionless POS validators to secure the network. With a set of staking management contracts deployed on Ethereum, anyone can stake MATIC on these contracts and join as a validator. However, one must currently stake approximately $20K of MATIC in order to become a top 100 validator. So entry is difficult. Validators are subject to rewards and slashing.
- Layer-2: L2s are built “on top” of the underlying L1 for the purpose of improving the latter’s scalability and efficiency. Polygon achieves lower gas fees and increased TPS for Ethereum by processing transactions on the Polygon chain, and then batching over in bulk the synthesized transaction data onto the Ethereum chain.
- Multi-Blockchain Network: The core of Polygon is the Polygon software development kit (SDK). The SDK allows third-party developers to create Ethereum-compatible side-chains and dApps that connect to Polygon’s main-chain and the larger Ethereum chain behind it. The amount of innovation happening with Polygon side chains is staggering. Polygon Edge (a particular software development kit iteration) is live. And multiple zk-rollups, optimistic rollups, and other scaling solutions are under development.
Cardano vs Polygon: Product Statistics
Cardano and Polygon both support NFTs, DeFi marketplaces, decentralized exchanges, gaming, metaverse, and payment dApps.
Cardano Product Statistics
- NFT Marketplaces: Approximately $165M in USD transactions since the beginning of 2022. Current daily USD transactions averaging $260K. Cardano NFTs mainly hosted via jpg.store.
- DeFi, Lending, and DEXs: Market cap of $77.86M locked across 9 projects. Minswap, Wingriders, and Sundaeswap collectively represent 89% of Cardano’s DeFi market.
- Web3 Gaming: Cardano’s gaming ecosystem is in its infancy. According to the statistics available, it appears that there are multiple games launched, but user numbers currently remain low.
Polygon Product Statistics
- NFT Marketplaces: $287M in USD transactions since the beginning of 2022. Current daily USD transactions averaging at $200K. Polygon NFTs hosted on OpenSea.
- DeFi, Lending, and DEXs: Market cap of $1.57B locked across 302 DeFi projects. Polygon hosts the DeFi heavy-weights AAVE, Curve, Uniswap, Quickswap, and Sushiswap.
- Web3 Gaming: Well-developed gaming ecosystem with 100K+ users across multiple games.
- EVM Compatibility: Polygon has realized and potential access to Ethereum’s rich dApp ecosystem.
ADA and MATIC: Tokenomics
ADA and MATIC are the native tokens for Cardano and Polygon, respectively. Both are used for transactions, network fees, staking, and governance. Both have differing issuance schedules, and initial and current token distributions.
ADA Tokenomics
- Max supply of 45B tokens. 34B (76%) are currently in circulation. ADA is an inflationary token with decreasing issuance over time. The current inflation rate is approximately 4.72%. The rate is estimated to be 0.9% by 2030.
- Approximately 73% of ADA tokens are staked.
- Initial coin distribution occurred from 2015 to 2017. The vast majority of coins (25.9B out of 31.1B) were sold to investors through a public token sale.
- Currently, 79.7% of ADA is in the hands of investors, while 16% is in the hands of IOHK, Emurgo, and the Cardano Foundation (the three centralized entities in charge of Cardano’s development).
MATIC Tokenomics
- Max supply of 10B tokens, all of which have technically been issued. 8.7B are currently in circulation, while the remaining 1.3B will be unlocked over the next few years via staking rewards.
- 36.2% of MATIC tokens are currently locked up in staking contracts.
- Initial coin distribution occurred in 2019 with 41.9% going to the Polygon team, advisors, and Polygon Foundation (centralized entities responsible for Polygon’s development).
- Currently, the share of tokens held by Polygon’s centralized entities has increased to approximately 42.5% of total supply.
Cardano vs Polygon Concluding Thoughts, Positives & Criticisms
Cardano vs Polygon, they are both technically sophisticated projects, but each are fundamentally different: Cardano (L1) is a direct competitor to Ethereum while Polygon’s (L2) central purpose is to directly support Ethereum.
A comparison of both projects reveals the following high-level positives and criticisms of each:
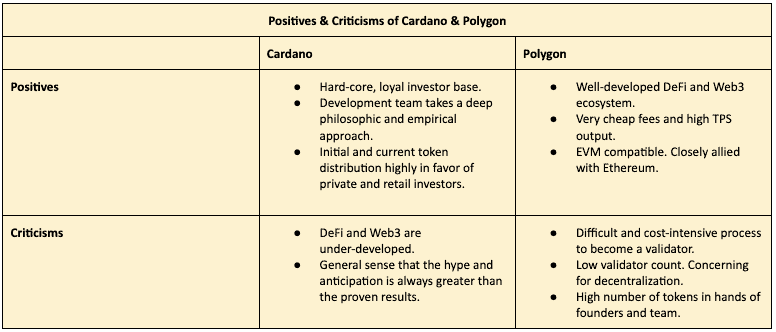
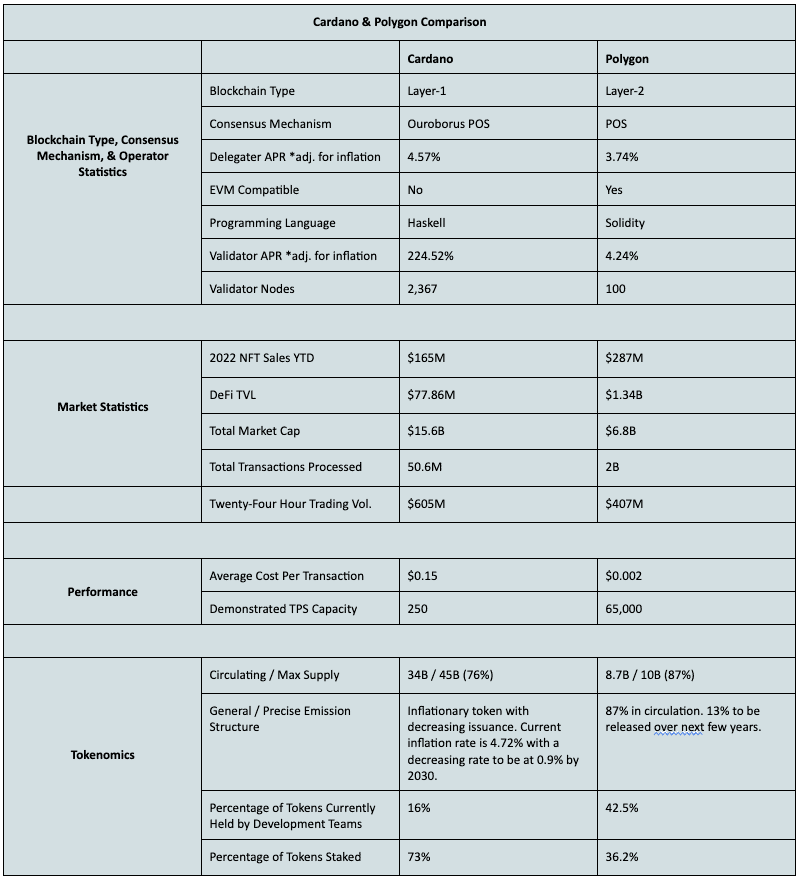
One interesting observation between these two projects is the mismatch in total market cap to use-case market cap. Cardano’s total market cap is twice that of Polygon. And yet, Polygon has a larger NFT marketplace, and dramatically larger DeFi TVL, total transactions processed, and Web3 applications.
This mismatch is likely due to Cardano’s extremely loyal fan-base. Cardano users have patiently stuck by the project through its slow roll-out process. Meanwhile, Polygon hasn’t quite attracted such an enthusiastic following, but regardless has still found success in bringing in persons to use the network.
We also compared Cardano vs Solana, check it out!