Cardano vs Solana: The Battle for Blockchain 3.0 Dominance

Ethereum broke new ground with the concept of smart contracts. But as a proof of work (formerly) chain performing 30 transactions per second (TPS), the market foresaw a need for more energy-efficient, faster networks.
Cardano vs Solana – known as version 3.0 blockchains – represent the next developmental iteration after Ethereum. If the future is multichain, then investors are wise to examine both, as each has made a name for itself and pushed blockchain technology forward in innovative ways.
The following analysis compares Cardano and Solana from conceptual, technical, product, and tokenomic perspectives. High-level positives and criticisms are provided in the conclusion. So LFG.
What Are Cardano and Solana
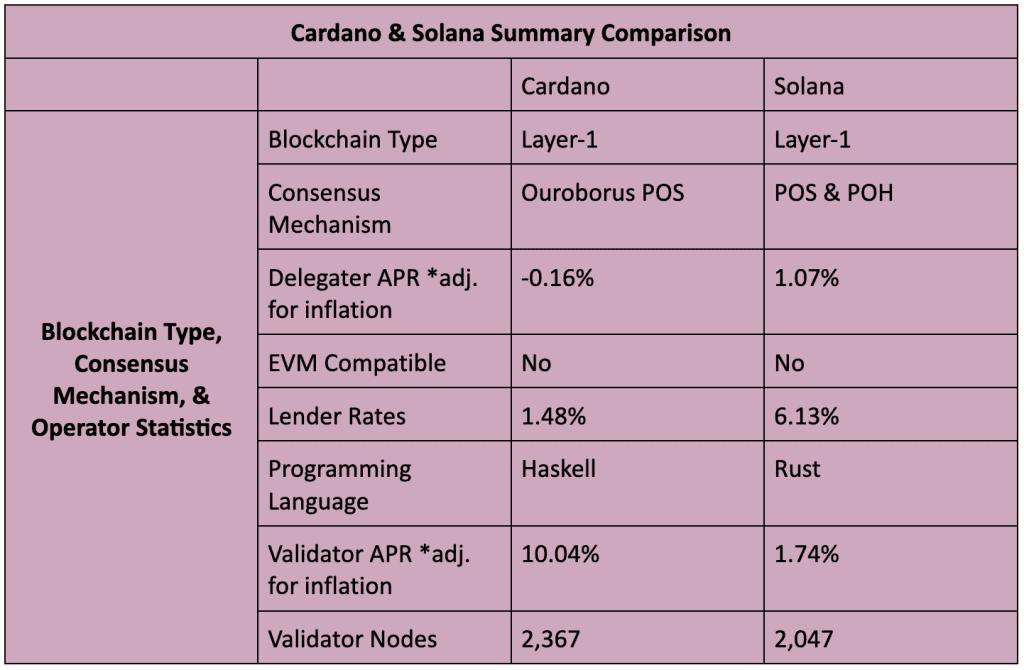
Cardano and Solana are decentralized, smart contract, proof of stake (POS), L1 blockchain networks. Both support diverse economic ecosystems and provide users with fast transactions and low fees. Both networks are in the top 10 crypto projects by market cap. Their native tokens are ADA and SOL, respectively.
How Do Cardano and Solana Work
While they seem similar, under the hood inspections reveal key conceptual and technical differences between the two networks. Here are the differences:
Cardano Concepts and Technicals
- Development, Research, and Philosophy: Cardano’s development has been slow and purposeful as the network is subject to extensive peer-reviewed research and testing. But, project developers have extremely ambitious hopes that the network will one day transform the global economy into a more financially inclusive system.
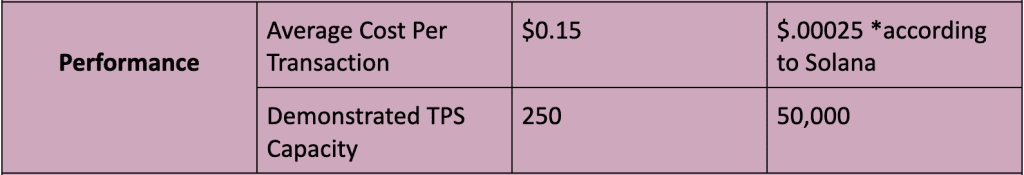
- Epochs and Slots: The Cardano blockchain is divided into epochs (approx. 4 days) and slots (approx. 20 seconds). The latter occurs inside the former. Ouroboros POS randomly selects nodes (odds in proportion to stake) to validate new blocks for each slot. Given an epoch can contain 432,000 slots, Cardano is able to process approximately 250 TPS.
- Ouroboros POS: “Ouroboros” is the ancient symbol of the snake that eats itself. Ouroboros POS implements a Global Random Oracle (GRO) which is essentially a randomly changing randomness algorithm. GRO leverages previous block data to help it change – hence the parallel to the symbol. GRO selects Cardano’s validators and is believed to provide enhanced network security due to the extreme difficulty in anyone correctly predicting how the algorithm will change.
- Sidechains: Cardano’s next stage (Stage Four: Basho) will usher in the development of sidechains – newly created blockchains that communicate and run in parallel with Cardano’s mainchain. The purpose of sidechains is to help the network scale. Thus, Cardano is becoming conceptually similar to Polkadot, which is a network of blockchain networks.
Solana Concepts and Technicals
- Hybrid POS and proof of history (POH): Solana implements a novel consensus mechanism that uses both POS and POH. Thus, the network is considered as one of the most technically advanced due to this hybrid nature.
- POS: Solana’s 2,047 validators are randomly selected to propose the next block. Selection odds are in proportion to stake. Other validators must either accept or reject the newly proposed block. If verified, the chosen validator receives a reward. Delegators are free to stake with any validator they like.
- POH: Solana produces extremely fast transactions because validators can efficiently verify the proper ordering of transactions with each other. Every validator runs a “cryptographic clock” that works in unison with every other cryptographic clock on the network. These clocks are synchronized because every validator can only commit one CPU to run the SHA-256 algorithm – the beating heart of each clock.
- Single Global State: Solana’s hybrid approach creates a blockchain so fast and efficient that there will be no future need for any sharding, scaling, or sidechain solutions. Thus, it’s intended that Solana will maintain a single global blockchain state. One blockchain – simple and seamless.
Cardano vs Solana: Product Statistics
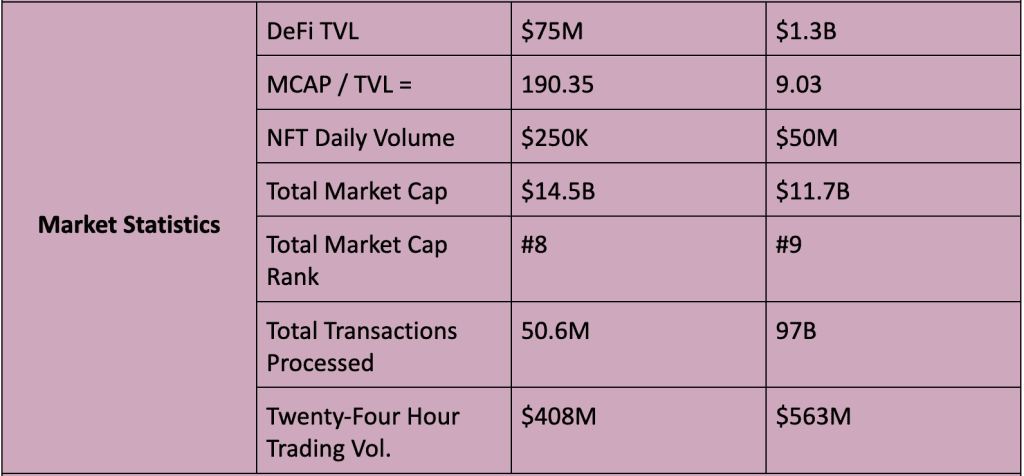
Cardano and Solana both support NFTs, DeFi marketplaces, decentralized exchanges, gaming, metaverse, and payment dApps.
However, data indicates that Solana’s ecosystem is much more developed than that of Cardano. MCAP / TVL is a useful formula to determine practical use of an ecosystem. The lower the number, the better. Cardano’s is 190 and Solana’s is 9. Thus, Solana’s economic utilization is roughly 21X that of Cardano.
Cardano Product Statistics
- NFT Marketplaces: Current daily USD volume averaging $250K.
- DeFi, Lending, and DEXs: Market cap of $75M locked across 12 projects.
- Web3 Gaming: Cardano’s gaming ecosystem is in its infancy. User numbers are very low.
Solana Product Statistics
- NFT Marketplaces: Current daily USD volume averaging $50M.
- DeFi, Lending, and DEXs: Market cap of $1.3B locked across 83 projects.
- Web3 Gaming: Solana’s gaming ecosystem is better developed with more users.
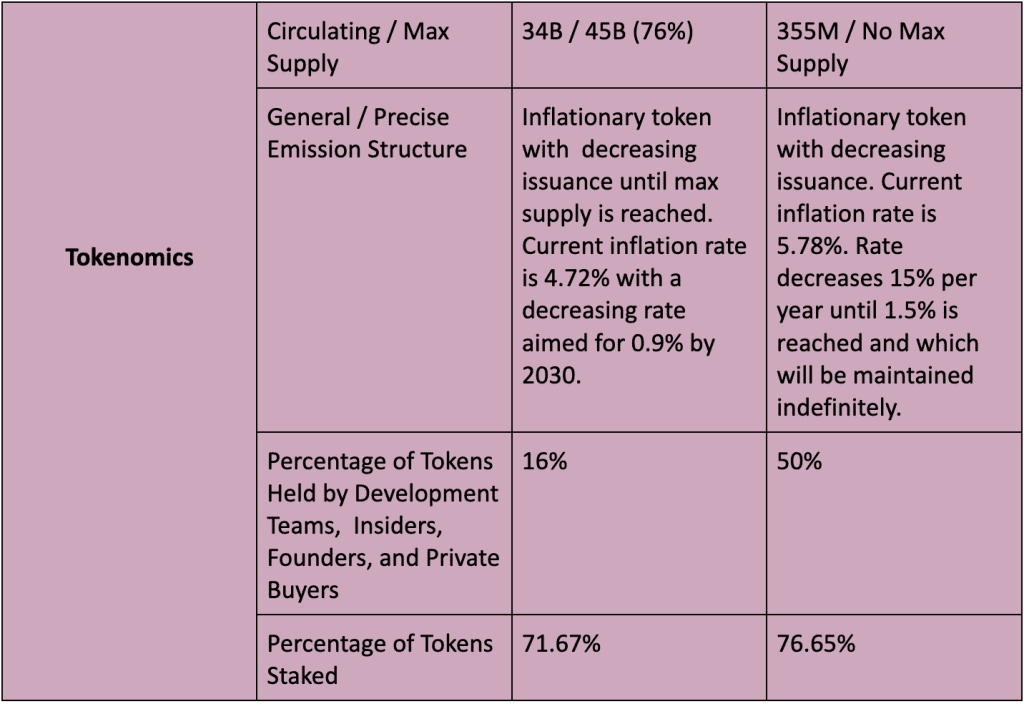
Cardano vs Solana: Tokenomics
ADA and SOL are the native tokens for Cardano and Solana, respectively. Both are used for transactions, network fees, staking, and governance. However, both differ significantly in terms of tokenomics, and initial and current token distributions. Data indicates that Cardano’s ADA has a more favorable tokenomic and distribution setup for retail investors.
ADA Tokenomics
- Max supply of 45B tokens. 34B (76%) are in circulation.
- ADA is an inflationary token with decreasing issuance over time. The current inflation rate is approximately 4.72%. The rate is estimated to be 0.9% by 2030.
- Approximately 71% of ADA tokens are staked.
- Initial coin distribution occurred from 2015 to 2017. The vast majority of coins (25.9B out of 31.1B) were sold through a public token sale.
- 79.7% of ADA is held by investors. 16% is held by Cardano’s founders and development teams.
SOL Tokenomics
- Current circulating supply of 352M. No fixed max supply.
- Inflationary token with decreasing issuance on a fixed schedule. Inflation rate is currently 5.78%. This rate decreases 15% per year until 1.5% is reached, which will then be maintained for the long-term.
- Approximately 76.65% of SOL are staked.
- Initial coin distribution occurred between 2019 and 2020. Four of the five sale rounds dealt exclusively with non-public buyers. An estimated 50% – 60% of the initial token distribution went to the development team, founders, insiders, and non-public purchasers.
- Currently, 50% of SOL is held by public buyers and the community reserve, while the other 50% is held by Solana’s founders, the development team, and private buyers.
Cardano vs Solana: Concluding Thoughts, Positives & Criticisms
Cardano and Solana are conceptual and developmental upgrades from Ethereum. Each introduced innovative technologies to the blockchain industry. Both chains have significant market share and many positives, but investors will want to know of the existing negatives with both projects.
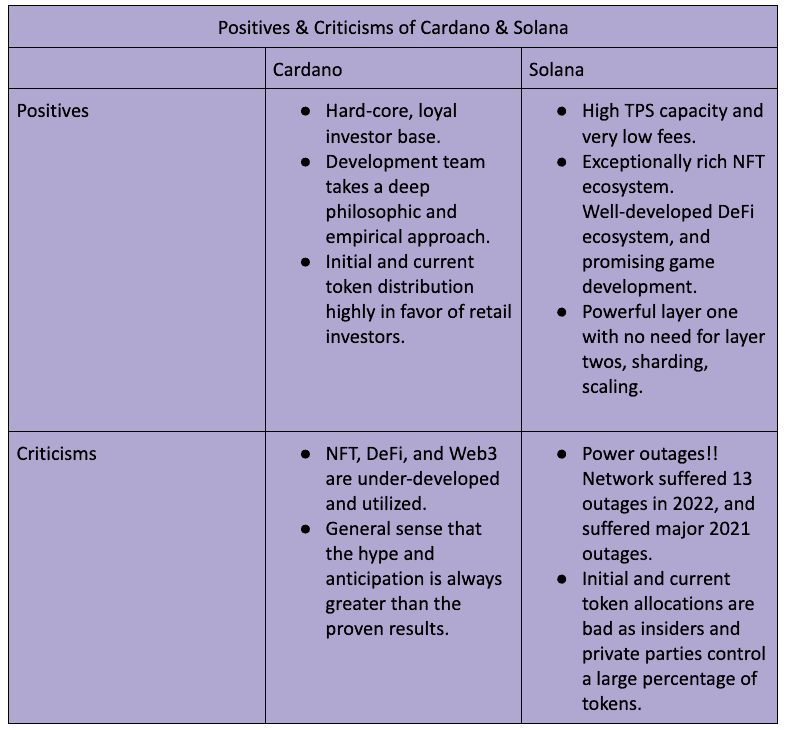
Cardano’s achilles heel is its inability to garner significant practical use, despite its large market cap. This contradiction (extremely high MCAP / TVL) is a double-edged sword. Clearly, Cardano has a loyal fan-base, shown by its high market cap. But its low TVL shows that the chain has been unable to achieve wide-scale practical use. Only time will tell if Cardano will be able to facilitate more wide-scale practical use-cases.
Solana’s major problem is its system-wide power outages. The system has suffered 13 outages in 2022. The latest occurred October 1st, when the network went offline for six hours due to one single misconfigured node. While the network prides itself on being a powerful single global state, one cannot help but wonder if this architecture is exposed to certain technical vulnerabilities, given the prevalence of outages over the past two years.
We also compared Cardano vs Polygon, we think that comparison might interest you as well!