Ethereum-Based Liquid Staking Ecosystem | 2023

“What’s the point of having cake if you can’t eat it.”
– Martin Hart, True Detective, Season 1.
At the time of this writing, Ethereum’s Shanghai – Capella upgrade is only hours away. Meaning, the 14% of ETH that’s been locked up for the last two years under Ethereum 2.0 will soon be free as birds.
Enter liquidity staking, which hit Cryptoville in 2020 and 2021. The free market invented liquid staking in direct response to ETH 2.0’s indefinite lockup period. A lot of economic value was getting locked away, and the free market wasn’t cool with it staying illiquid.
Liquid staking is an interesting crypto sub-industry, and one I believe will only continue to grow. This article explores the Ethereum-based liquid staking ecosystem, specifically:
- The key players;
- What is liquid staking, where the value comes from, what are the benefits and risks;
- the three prominent Ethereum liquid staking protocols: Lido, Rocket Pool, and Frax Finance.
Let’s dive in.
Overview of the DeFi Liquid Staking Ecosystem
Looking down at the DeFi liquid staking ecosystem at an altitude of 50,000 feet, the main components are the following:
- Liquid Staking Protocols: dApps that receive and stake users’ assets to proof-of-stake networks. These dApps issue back to users liquid staking derivatives, in proportion to the amount of assets received. These dApps ensure users’ staking rewards are accounted for and release the staked assets back to users when the derivatives are returned.
- Liquid Staking Derivatives: Tokenized receipts of the staked assets. These receipts represent users’ shares of the staked assets and accrued rewards. The free market typically values these derivatives equal to that of the underlying assets. Thus, these derivatives are “liquid”. Users can deploy them across DeFi for trading, lending, collateral, staking, and in liquidity pools.
- Protocol DAOs and Tokens: Most of these protocols are governed by decentralized autonomous organizations (DAOs). DAOs typically use direct-democracy voting via governance tokens. The free market determines the value of these tokens.
- Related Third-Party dApps: Any other third-party DeFi dApp that offers a product or service associated with the liquid staking derivative. Typical examples would be DEXs, lending and borrowing protocols, and staking or aggregator protocols.
What is Liquid Staking
Liquid staking is the process of:
- Staking ones crypto-assets through a liquid staking protocol.
- Receiving liquid staking derivatives in return
- Using those derivatives in other DeFi applications
- All while still capturing the staking rewards of the underlying asset.
Let’s look at why these derivatives have economic value, and the benefits and risks of liquid staking.
Why Liquid Staking Derivatives = Economic Value
Liquid staking derivatives have economic value because the free market says so. But why would the free market say so? It’s actually very simple:
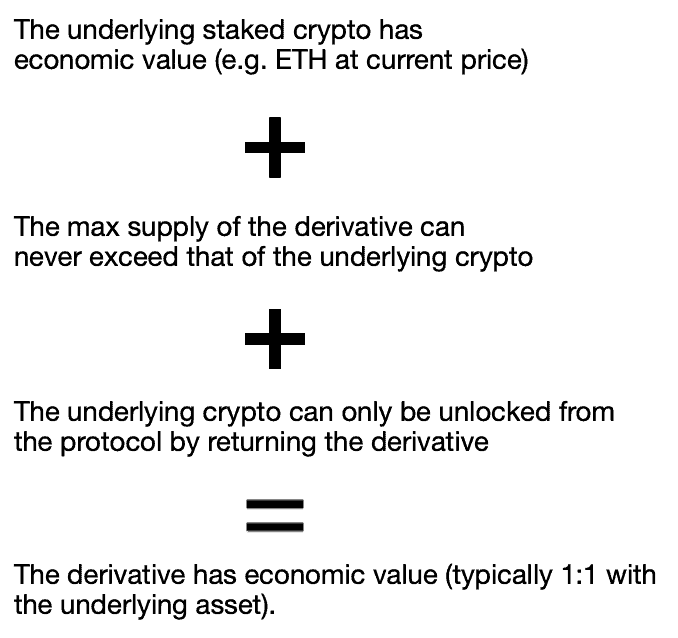
Note: Protocols only mint and distribute these derivatives in direct proportion to the amount of underlying crypto that they receive.
Benefits
Easy. You get your cake and can eat it too.
Liquid staking derivatives allow users to receive the staking rewards from their crypto assets, while simultaneously giving users the ability to use their derivatives for other purposes across the DeFi. Basically, these derivatives provide users with 2X leverage on their staked assets.
Risks
Yes please. Mistreat your cake, and it eats you.
The central rule here is if the derivative is lost, the underlying staked assets are lost. Remember, the underlying assets cannot be released from the protocol without returning the derivatives.
With that in mind, here’s the major risks factors, sorted (in my opinion) from greatest to least risk:
- Doing anything that results in you “losing” your derivatives (e.g. sending them to a wrong address, using them as collateral or leverage and getting liquidated, etc.).
- Low Market Liquidity: The trading market for derivatives is currently about 200X smaller than of the underlying assets. Tight liquidity conditions could, at times, make trading or obtaining a 1:1 price difficult.
- De-Pegging: The free market determines a derivative’s value. Periods of market volatility or uncertainty have caused derivatives to de-peg (e.g. stETH deviated 7% below ETH’s price in mid-2022 (the valuation eventually returned 1:1)).
- Governance and Protocol Risks: The protocol could pass a foolish decision that causes the market to discount derivative’s value. Or the protocol could act negligently or recklessly, resulting in some of the staked assets getting slashed by the network.
- Smart Contract Bugs or Hacks: If a technical issue affects the smart contract that operates the derivative, the underlying assets could be lost.
Protocols, Liquid Staking Derivatives, and DAO Tokens
Let’s turn to three of the most prominent Ethereum liquid staking protocols. For each, we will look at how the protocol works, the derivative, the DAO, and governance token.
Lido

Not only is Lido Ethereum’s largest liquid staking protocol, but Lido is the largest DeFi protocol in the crypto-economy. At the time of this writing, Lido has $11.3B in total value locked (TVL).
Lido operates across five blockchains. However, most to the action is happening on Ethereum. Users give their crypto to Lido, Lido stakes the crypto on the applicable chain, and issues to the users a derivative (stETH for Ethereum). Lido is governed by a DAO, and LDO is the governance token.
stETH’s major uses cases are liquidity provisioning on Curve, lending and borrowing on Inverse Finance, and staking, farming and trading opportunities on other third-party dApps. stETH is battle-tested, but it did suffer that 7% depeg. So it’s not immune to market instability either.
The Lido DAO is busy. This is a functioning, complex, blockchain government. Committees, research forums, regular and emergency track voting. And tons of proposals.
But LDO is a pure governance token. There’s no staking opportunities. And most of the major bag holders are VCs, whales, and the Lido team. So unless you’re a multi-millionaire with a deep interest in helping govern the platform, buying LDO tokens for governance is akin to throwing spare change in a wishing well. However, LDO will pump on hype and narrative, so money can be made riding those waves.
Rocket Pool

Rocket Pool is a highly decentralized, open source, Etheruem-based protocol. It’s more decentralized than Lido, because node operator barriers to entry are lower (i.e. one only needs 16 ETH to validate, instead of 32). Thus, Rocket Pool features more node operators with less concentrated amounts of ETH between them. Rocket Pool uses open source smart contracts. Anyone can inspect them.
But most users will simply stake their ETH through Rocket Pool. The minimum amount required is 0.01 ETH. In return, Rocket Pool issues back rETH. Similar to stETH, rETH can be used for trading, liquidity provisioning, lending, borrowing, and staking. However, rETH’s 24 hour trade volume is 10X smaller than stETH.
Rocket Pool has the Oracle DAO and the Protocol DAO. The Oracle DAO handles the protocol’s technical operations, while the Protocol DAO deals with the protocol’s administrative and planning functions. RPL is the governance token. But it also serves as a stick and carrot incentive for node operators.
- Stick: Operators must stake a certain amount of RPL as collateral on the network. This RPL can be slashed in the event that a node operator misbehaves.
- Carrot: Operators are rewarded with additional RPL for their staking services.
Thus, RPL is a governance and utility token and offers retail investors with some staking opportunities.
Frax Finance

Frax Finance is a decentralized stable-coin protocol. The platform offers three products: FRAX (a USD stablecoin), the Frax Price Index (a stablecoin pegged to a basket of consumer goods), and frxETH, a ETH liquid staking derivative. The protocol is DAO governed, and uses the FXS token for voting power.
Frax Finance has a two step process for receiving an ETH derivative that captures the accruing staking reward:
- When users send their ETH to Frax, and the protocol stakes the ETH, mints, and returns frxETH to the users. frxETH is 1:1 pegged with ETH.
- Users can then stake their frxETH back to Frax, and will receive in return sfrxETH, a synthetic derivative of frxETH (I know, sorry). Importantly, sfrxETH is what accrues the staking yield of the underlying ETH.
Long story short, sfrxETH is the rough equivalent to rETH and stETH. Although there is an active DeFi market both for frxETH and sfrxETH.
Frax Finance’s governance token is FXN. However, FXN is also integral to the economic functioning of the protocol. This means it also offers staking opportunities. The FRAX stable-coin is collaterally and algorithmically backed. FXS is used to help FRAX maintain its dollar peg via a seigniorage mechanism. Thus, FXS captures economic value as both a governance token but also as a utility token for its central role in the protocol.
Conclusion
If you’re willing to accept the risks, liquid staking can give you the ability to collect staking rewards while also leveraging your staked crypto throughout DeFi. Most of the action is on Ethereum. And Lido, Rocket Pool, and Frax Finance are slinging most of the derivatives.
Back to Ethereum’s Shanghai – Capella upgrade. Cryptoville is speculating about what it all means for Ethereum’s overall staked supply and ETH’s price. Not financial advice, but I think the amount of staked ETH on the network only increases after the upgrade. And liquid staking is one of the reasons. I think some will un-stake their ETH from the Beacon chain only to immediately re-stake it via a liquid staking protocol.














Responses