What are Crypto Tokens? | Tokens vs Blockchains Explained for Beginners

Tokens vs. Blockchains
The differences between Blockchains and Tokens are a fairly simple thing to understand. Blockchains like $BTC Bitcoin, $ETH Ethereum, and $SOL Solana have Coins to represent this very first layer of the protocol. Crypto tokens represent property issued on these Blockchain Networks.
For instance, an infinite amount of ERC-20 Tokens can be issued on the Ethereum Network in one day. But, there are limits to how many $ETH Coins can be mined every day. While Emission Rates maintain a Coins supply and economics on Ethereum, no such thing exists for all the Tokens operating on the Solana Network.
While developers of Tokenized projects can and do create supply limits, you have to understand that this is still effectively creating something from nothing. Tokens operate on top of their respective Blockchain Networks.
Additional Risk with Tokens
While Coins maintain their own individual risk factors, when you invest in Tokens you’re more than doubling your exposure to risk. The reason for this is that you have to think of the base layer of a Network like Ethereum as a 10×10 box. Within this is another 2×2 sized box. These boxes represent the price of both assets.
When you buy $ETH you only have to worry about one price. But, when you buy an Ethereum Token you have to factor in both the price of $ETH and the Token you’re purchasing. As the price of $ETH rises so will the price of all underlying tokens, if only briefly. This even happens with Stablecoins before quickly rebalancing.
The opposite goes for when the price of $ETH declines. This symbiotic relationship between Parent Coins and Child Tokens only works in one direction. When a random ERC-20 Token appreciates 100% in a day, ETH price is not directly affected.
Fungible vs Non-Fungible Tokens
While all Coins are considered Fungible. Tokens can be Non-Fungible as well as Fungible. When you hear something referred to as Fungible it means that each one is an exact copy of the next. When there are distinct differences between them, these are considered Non-Fungible.

As no two are alike, this has created a category called NFTs or Non-Fungible Tokens. Things like artwork, unique gaming accessories, and decentralized finance are all possible due to the ability of Blockchain Networks to create Non-Fungible Tokens.
One is not necessarily more important than the other when discussing Blockchains and Tokens. In the same box example made previously you could argue that $ETH is also contained within a 50×50 sized $BTC box. As everything in Blockchain fundamentally moves to the rhythm of Bitcoin.
Blockchain Forks
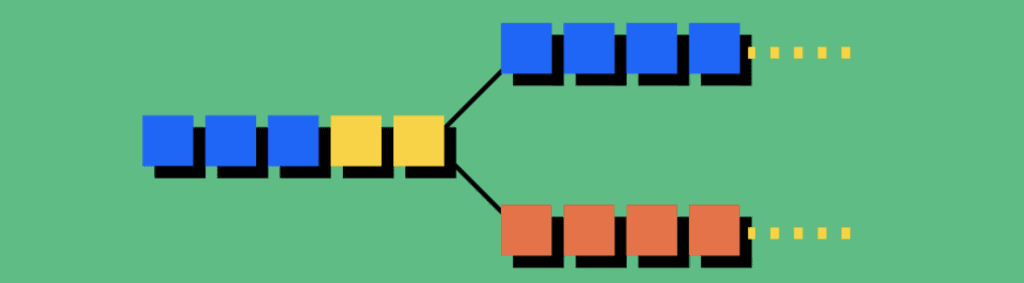
While Bitcoin doesn’t have any Tokens operating on the Bitcoin Network, there have been instances where disagreements happen on the Bitcoin network and instead of Tokens being issued to pursue a new use case, the Bitcoin Blockchain code is copied and forked to a separate Blockchain like Bitcoin Cash where all holders of the original Bitcoin are given an equal amount of the new Blockchains Coins, while the original Bitcoin Blockchain continues doing what it’s always done.
This happened to Ethereum but when the Blockchain split, the newer Ethereum Blockchain became the accepted version and $ETC Ethereum Classic was created to represent the old Blockchain.










