What are Smart Contracts? | Crypto Smart Contracts Explained for Beginners

What are Smart Contracts?
Smart contracts are programs stored on the Blockchain that will only operate their intended function if certain conditions are met. In 1990 Nick Szabo first proposed smart contracts as “a set of promises, specified in digital form, including protocols within which the parties perform on these promises”. Ethereum introduced this technology with its Blockchain in 2015 and these Digital Contracts are solely responsible for the creation of DeFi (Decentralized Finance) and NFTs (Non-Fungible Tokens).
While one could argue Bitcoin was the first DeFi integration, Bitcoin is not because Bitcoin is hard money. These Smart Contracts have the general purpose of automating the execution of agreements between multiple parties but they themselves are not sound money.
With Crypto Smart Contracts, multiple people use computers to engage in commerce with one another and everyone is guaranteed the agreeably programmed outcome. Hard to believe, and even harder to understand is the incredible amount of human capital and energy that has gone into this technology, in such a short period of time. Any new technology inherently comes with its set of bugs, solutions, exploits, and advancements. But, it’s easy to see that Smart Contracts are never going away, and here are some reasons why.
Why Do We Need Smart Contracts?
Humans are, and always will be, human. By design, we’re flawed and susceptible to making mistakes and miscalculations. The probability of code deviating from its written function is almost zero.
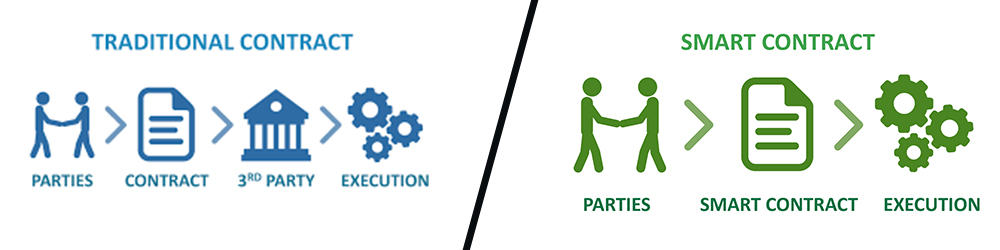
Smart Contracts simply execute agreements. But, in doing so they remove the need for trusted intermediaries, arbitration, fraud losses, as well as the massive reduction in malicious and/or accidental intentions.
The term itself “smart contract” has been more specifically applied toward the notion of general-purpose computation that takes place on a blockchain or distributed ledger instead of legal agreements, but it’s more of a means of performing obligations based on existing agreements like payment obligations.
A Smart Contract also can be regarded as a secured storage procedure as its execution and transfer of value between parties are strictly enforced and can not be manipulated. After a transaction with a specific contract, details are stored on the blockchain. This is because the actual execution of smart contracts is controlled and audited by the operating platform itself, not by any arbitrary server-side programs connecting to the platform.
The ERC-20 Smart Contract
Similar to a transfer of value on a blockchain, deployment of smart contracts occurs by sending a transaction from a wallet for that specific blockchain.
One of the most significant smart contract standards on Ethereum is known as ERC-20, which has emerged as the technical standard used for all smart contracts on the Ethereum blockchain for fungible token implementations.
The ERC-20 standard for Ethereum defines a common list of rules that all fungible Ethereum tokens should adhere to. Consequently, this token standard empowers developers of all types to accurately predict how new tokens will function within the larger Ethereum system. This simplifies and eases developers’ tasks, allowing them to proceed with their work, knowing that each and every new project won’t need to be redone every time a new token is released, as long as the token follows the rules. These are just some of the great things about smart contractsb










