BitVM: Is there a Use Case for Complex Smart Contracts on Bitcoin?

TL;DR
BitVM is a proposal that will make it possible to create and run complex smart contracts that settle on the Bitcoin blockchain. A healthy dose of skepticism feels appropriate here – after all, why compete with Ethereum and its Layer 1 kin on a turf that is firmly theirs? But on closer inspection, there might be something to be said for niche-type smart contracts that rely on the most secure chain of them all.
BitVM is short for Bitcoin Virtual Machine. Released in early October 2023, BitVM’s white paper details the technological implementation of this promising idea. Ethereum was the first blockchain to make such a virtual machine possible: a platform for potential decentralized applications (dapps), an operating system if you will, on a blockchain.
To run dapps, you need smart contracts. A smart contract is like an automated agreement or a set of programmed rules. Imagine you and a friend making a bet on the outcome of a sports game. With a smart contract, you can program these rules into a computer system, which watches the game’s outcome and when the result is clear, it automatically sends the money to the winner.
Basic smart contracts already exist in Bitcoin. But, for simplicity’s sake and security reasons, they have been limited to fundamental operations like multi-signature transactions, timelocks and payment channels such as those used in the Lightning Network. Very handy, but not comparable to what for example Ethereum smart contracts can pull off (think: complex automated market makers of decentralized exchanges).
What are the Characteristics of BitVM?
BitVM introduces an innovative framework for developing more complex and expressive smart contracts on Bitcoin.
As an introduction, some key points of BitVM:
- Most of the processing in BitVM happens off-chain, making operations more efficient and unbothered by overcrowded and expensive Bitcoin blockspace. In this sense, BitVM differs from the Ethereum Virtual Machine, which runs on-chain.
- Unlike Ethereum’s virtual machine (EVM), BitVM is designed to favor two-party transactional exchanges. This is a limiting factor.
- Still, BitVM is Turing complete. Without going into the details of Turing completeness, it means you can deploy very complex smart contracts on it.
How does BitVM Work?
Like so many recent Bitcoin innovations (Ordinals, for example) BitVM leverages the functionality of Bitcoin’s Taproot upgrade, which went live in November 2021. BitVM uses a system that blends fraud proofs and the so-called challenge-response protocol to handle and authenticate transactions between two entities: the prover and the verifier.
- The prover starts a computational process and transmits it through the channel they share with the verifier.
- The verifier then assesses and confirms the accuracy of this computation.
- After this verification, the transaction gets included in a collective batch that is posted on the Bitcoin main chain.
A quote from the introduction of the BitVM whitepaper:
‘Rather than executing computations on Bitcoin, they are merely verified, similarly to optimistic rollups. A prover makes a claim that a given function evaluates for some particular inputs to some specific output. If that claim is false, then the verifier can perform a succinct fraud proof and punish the prover. Using this mechanism, any computable function can be verified on Bitcoin.’

Who would have thought good old Bitcoin would lend technology from optimistic rollups tech like Arbitrum and Optimism. This is nothing to scoff at, of course: it shows a progressive mindset that the Bitcoin community can use. See also the proposal of zk-rollups on Bitcoin, a technology that is in principle related to optimistic rollups, as it offloads computationally intensive work from the Bitcoin blockchain to a separate layer, the proof of which is submitted on-chain.
Skepticism about BitVM
That’s all well and good. But still: why would Bitcoin bother with venturing out beyond its niche of sound money? Blockchain connoisseur and freedom maximalist Andreas Antonopoulos is skeptical of different blockchains projects trying to compete on each other’s turf.
In the same way that Ethereum was in his view a bit foolish to compete with Bitcoin in the sound money department – heck, Ethereum tried to outdo Bitcoin, claiming it is ‘ultrasound money’ – Bitcoin in his view has no business competing in the smart contract design space.
The analogy often used by Antonopoulos is that Bitcoin is a hammer and Ethereum a drill. A good craftsman for which jobs to pick up which tool.
‘If you want to make small circular holes in wood, don’t use a hammer. ‘But what about if we use a wheel with a thousand hammers that hit a drill-bit repeatedly?’ You’ve made a very wasteful hammer.’

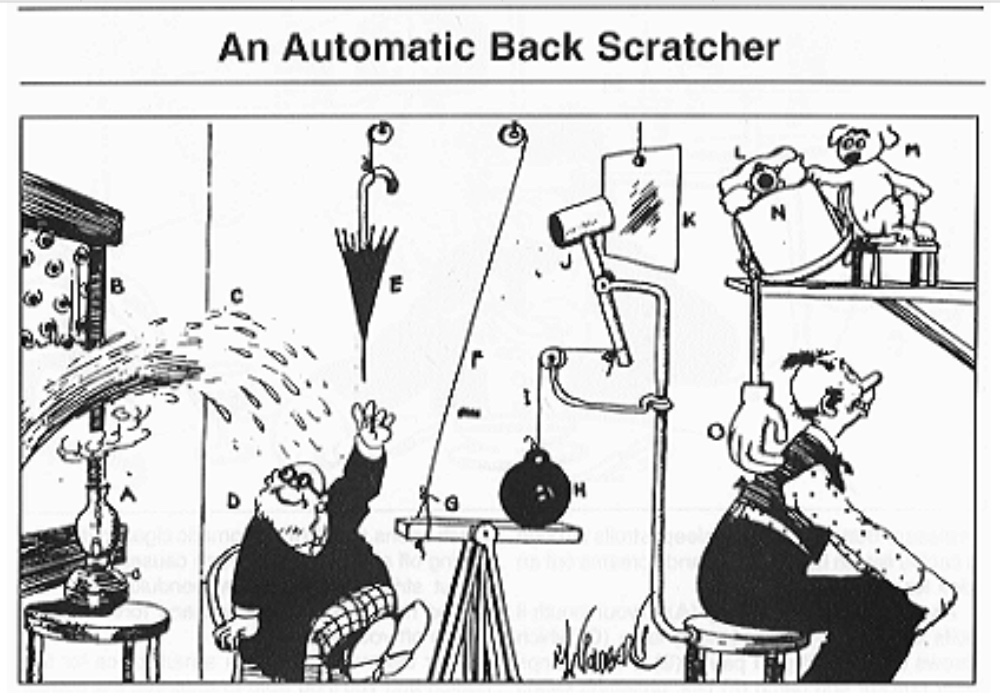
It reminds me of Rube Goldberg contraptions, which are carefully designed to perform a simple task by triggering a complex sequence of chain reaction events.
Indeed, the question is if we need a better way of making smart contracts than Ethereum already does – or other Layer 1s for that matter. The underlying question here is: are smart contracts preferable when they are built on sound money? Bitcoin maxi’s will have their opinion. But the fact is that the market has already answered this question. In the past five years, there has been mass adoption of smart contracts on other chains than Bitcoin.
Indeed, imagine buying a ticket NFT for a concert next week. You probably won’t worry too much about the soundness of the base layer. What’s the worst that could happen if let’s say something goes wrong with Avalanche?
Use Cases for Advanced Smart Contracts on Bitcoin
So, is BitVM the equivalent of a Goldberg contraption: ingenious but useless? I’m not sure. One can also imagine use cases for which at least some market participants would prefer smart contracts on Bitcoin. Why? First of all: ease of use. Since BTC is the most widely adopted crypto, there are more financial services and products built around it. Users who want to deploy smart contracts that need to interact with these services might find it easier to do so on the Bitcoin blockchain.
And then there are types of smart contracts that involve very large sums of money, or smart contracts that are expected to span years or even decades. Would you run these on any hot new layer 1 or would you prefer Bitcoin as the settlement layer for your will or trust?
Conclusion
It’s clear that Bitcoin is currently limited in its smart contract functionality and BitVM would be a quantum leap. Time will tell if BitVM – if implemented – will become a gloriously useless Rube Goldberg contraption or if it will be in demand for specific types of smart contract functionality. It’s conceivable that it will play a role in decentralized exchanges, fintech apps, and supply chain industries. As long as these apps don’t rely on multi-party functionality.